An Overview to Computer Graphics
Computer Graphics
To synthesis and manipulate visual information.
Application
- Video Games: Technically, global illumination determines the quality of the game performance: the lighter the graphics shows, the better the game is.
- Movies: Special effects
- Animations: Simulate particles in different scenes.
- Design
- Visualization: One of the way to manipulate visual information.
- Virtual Reality & Augmented Reality
- Digital Illustration.
- Simulation: physical simulation, computation and implementation.
- Graphical User Interface
- Topography
Fundamental Challenge
- Require understanding of all aspects of physical world
- Create and interact with realistic virtual world
- Computing methods, displays, technology.
Topics
Rasterization
- Project
geometry primitives(3D triangles/polygons) on to the screen. - Break projected primitives into
fragments(pixels) - Gold standard in Video Games (Real-time Applications)
Real-time/offline computer graphics: more than 30 fps (frame per second)
Curves and Meshes
How to represent geometry in Computer Graphics
- Bezier Curve
- Catmull-Clark subdivision
Ray Tracing
- Shoot rays from the camera through each pixel
- Gold standard in Animations / Movies (Offline Application)\
Animation / Simulation
- Key frame animation
- Mass-spring System
CG vs CV
Difference
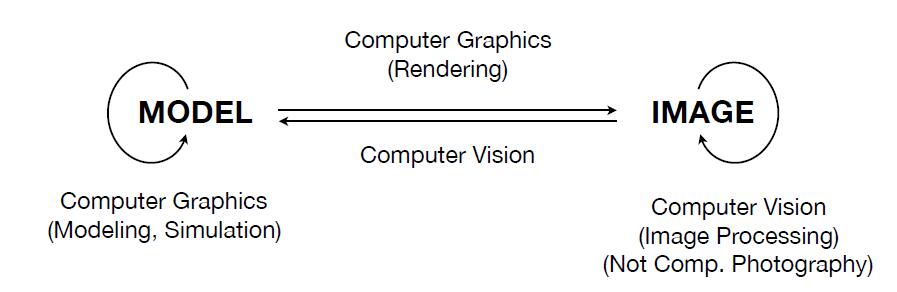
-
Computer Vision is to understand, recognize and predict the content of images.
-
Computer Graphics is to model and simulate the geometry of visual information.
Geek = Genius + Freak
Reference
PREVIOUSMaterial